Canmore wildlife - cougars

Alberta is home to a healthy, self-sustaining population of cougars. Canada's largest cat, the cougar, is an elusive creature living primarily in southwest Alberta.
Cougars are recognised for their extraordinary hunting abilities, beauty, strength and their rare appearances, and it is unlikely that you will ever catch a glimpse of a cougar in its natural habitat, although current estimates for some areas of southwest Alberta suggest that there may be up to four cougars per 100 square kilometres. Because of its elusive nature, conflicts with humans have historically been rare.
Felis concolor, the species name, literally means one colour, although cougars can be several different shades of golden/yellowish brown depending on their environment.
Cougars are known by a variety of names: puma, mountain lion, catamount, and even, although rarely, as panther.
Cougar facts:

- their primary food source is deer as it is more energy efficient to hunt one large animal rather than several smaller ones
- as opportunists at the top of the food chain, cougars will also huntelk, moose, sheep, livestock, hares, beaver and grouse
- cougars are crepuscular meaning they are most active at sunrise or sunset, but will also hunt at any time of day or night if required
- they prefer to sleep in dens on ledges, under fallen logs, between rocks or in tree hollows on steep slopes
- cougars are houseproud, never littering their den with bones or other detritus
- a single cougar can roam up to 80 km in one day, and usually have ranges up to 300 sq. km
- cougars normally mate between March and June, but have been known to mate at other times of the year
- the female cougar gives birth 3 months after mating, to a litter of 1-6 kittens, she will nurse them for 3 months before introducing them to meat
- cougar kittens remain with their mother for up to 2 years
Cougar characteristics:
- cougars can reach weights between 65-90 kg for males, and 40-60 kg for females
- they have very long tails, 150cm in length, which they use for balance
- their hind legs are longer than their forelegs to develop greater leaping power
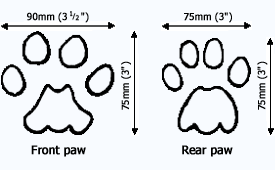
- cougars front paws are larger than their rear
- cougars possess a field of vision covering 130°, which makes they very well equipped for detecting prey
- their night vision is enhanced by having an extra large pupil to gather light, and a special layer that reflects the light back through the visual cells of the eye, during daylight the pupils contract to a vertical slit to protect the eye
- cougar tracks rarely show evidence of claws, although distinctively in snowy areas tail marks in the snow can be seen

Cougar paw prints: